| found: 795 books on 53 pages. This is page 29 Previous page - Next page |
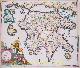
New Netherland, New Amsterdam (New York) - Justus Danckerts, 1690
Novi Belgii Novaeque Angliae Nec Non Pennsylvaniae et Partis Virginiae Tabula (Map of New Netherland, New England, as well as Pennsylvania and a part of Virginia.) Copper engraving published by Justus Danckerts in Amsterdam in 1690. With original hand colouring. Size: 46.5 x 54.4 cm. At the end of the 16th century, knowledge of the North American coast was still very incomplete in Europe and in The Netherlands. There was an idea that the Pacific and Atlantic oceans were connected by a river that ran through the American continent. The reason for the first Dutch trading voyages to the land that would later be called 'New Netherland' were the discoveries made by Henry Hudson in 1609. In that year, the famous English explorer sailed to the Arctic Ocean. He had been commissioned by the Dutch East India Company (VOC) to attempt finding a shorter route to Asia. However, Hudson interrupted his efforts and set course for North America, where he discovered a large river, which still bears his name. Interest in this area was sparked in the Netherlands, and lucrative prospects for the fur trade (including beaver hides) ignited the entrepreneurial spirit of the Dutch. Different groups of merchants tried to outdo each other. From 1611 to 1614, they each organized their own expeditions to explore this unknown territory. One such figure was Captain Adriaen Block. On behalf of thirteen merchants, he sailed in 1613 to the 'Great River' (today's Hudson River) with the intention of further exploring the trade possibilities of the area. Block returned to the Netherlands with positive stories about the economic potential of this territory. The States-General were also impressed. On October 11, 1614, they granted the "Nieuw-Nederland Compagnie" a trade charter. The united merchants were authorized by the States-General to make four trading voyages to New Netherland. There was no extension of this trade monopoly. The economic interests of this part of the world had become so significant for the Netherlands that in 1621, the States-General established the Dutch West India Company (WIC). Nicolaes Visscher created a map in 1651 based on the manuscript map made by Adriaen Block during his exploratory journey, which he included in his atlases. The copper plate was reused in 1655 by Jan Jansson and once again brought to market "multis in locis emendata" (corrected in many places) in 1690 by Justus Danckerts. In Danckerts' particular copy, the course of the Delaware River has been completely revised, and Pennsylvania is now correctly named. Compared to Visscher's map, Danckerts adorned his map with more wild and farm animals, hence the map is often referred to as the "Farm Animal Map". The land was meant to look more appealing to settlers. The famous view at the bottom right of the map of "Nieuw Yorck eertyds genaemt Nieuw Amsterdam op 't Eyland Manhattans" (New York formerly called New Amsterdam on the Island of Manhattan) was first published around 1650 by Joan Blaeu. The Dutch flag fluttering ("this flag is raised when ships come into the harbor") appears to be directed to the States-General to urge the Dutch West India Company for additional support for the colony in New Amsterdam. However, by the time Danckerts published the map in 1690, it was already too late. From 1664, the settlement was in English hands. Price: Euro 6.500,- (incl. frame)
 Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional seller
Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional sellerBook number: 8322
€ 6500.00 [Appr.: US$ 7033.53 | £UK 5529 | JP¥ 1103126]
Keywords: Danckerts-- Justus
Norway - Cornelis Danckerts, c. 1696
Norvegia Regnum Divisum in suos Diocaeses Nidrosiensem, Bergensem, Opsloensem, et Stavangriensem. Et Praefecturam Bahusiae. Engraved double-page map in beautiful original colour, published in Amsterdam approx. 1696 by Cornelis Danckerts. Size: 58 x 50 cm. The maps shows us the southern part of the Kingdom of Norway divided into the Diocese of Nidaros (today's Trontheim), Bergen, Oslo, and Stavanger and the prefecture of Bohuslän (Båhuslen). There is an inset map of northern Norway in the upper left corner showing the Finnmark region?. The 17th century saw a series of wars between Denmark–Norway and Sweden. The Kalmar War between 1611 and 1613 saw 8.000 Norwegian peasants conscripted. Despite lack of training, Denmark–Norway won and Sweden abandoned its claims to the land between Tysfjord and Varangerfjord. With the Danish participation in the Thirty Years' War in 1618–48, a new conscription system was created in which the country was subdivided into 6.000 legd, each required to support one soldier. Denmark–Norway lost the war and was forced to cede Jämtland and Härjedalen to Sweden. The Second Northern War in 1657 to 1660 resulted in Bohuslän being ceded to Sweden. The Danish monarch elevated himself to absolute and hereditary king of Denmark (including Norway) in 1661, eliminating the power of the nobles. A new administrative system was introduced. Departments organized by portfolio were established in Copenhagen, while Norway was divided into counties, each led by a district governor, and further subdivided into bailiwicks. About 1,600 government officials were appointed throughout the country. This map was made when Ulrik Fredrik Gyldenløve was viceroy of Norway. It is embellished by a depiction of Neptune and a mermaid below the title cartouche and crowned with the Norwegian coat of arms. The Danckerts family were notable print and map sellers, and engravers in Amsterdam for nearly a hundred years, between 1630 and 1727. Between 1680 and 1700, Justus an his three sons Cornelis, Theodorus, Justus II published several editions of their Danckerts Atlas. Their maps were in demand for the wonderful decorative quality of their engraving rather than for their accuracy. Price: Euro 725,-
 Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional seller
Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional sellerBook number: 1515
€ 725.00 [Appr.: US$ 784.51 | £UK 616.75 | JP¥ 123041]
Keywords: Danckerts-- Cornelis
Peloponnese - Justus Danckerts, 1684
BEAUTIFUL MAP OF THE PELOPONNESIAN PENINSULA "Peloponnesus Hodie Moreae Regnum" [Peloponnese known today as Kingdom of Morea], copper engraving published by Justus Danckerts in Amsterdam, 1684. Original hand colouring. Size: 50,9 x 59,5 cm. The map was engraved during the Great Turkish War between the Ottoman Empire and the Holy League consisting of the Holy Roman Empire, Poland-Lithuania, Venice, Russia, and Habsburg Hungary. Intensive fighting began in 1683 and by 1687 the Venetians occupied the entire peninsula, and received recognition by the Ottomans in the Treaty of Karlowitz (1699). The Venetians established their province as the "Kingdom of the Morea". (The Ottomans however, reconquested the peninsula in 1715.) The momentary victory is depicted in the cartouche where a triumphant Venetian lion (winged, with open book and halo around its head) swings its sword whilst captured Ottomans lie at its feet. Price: Euro 950,-
 Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional seller
Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional sellerBook number: 1638
€ 950.00 [Appr.: US$ 1027.98 | £UK 808.25 | JP¥ 161226]
Keywords: Danckerts-- Justus
Belle Epoque fashion - Jules David, 1877
ELEGANTE DAMES IN HET BOIS DE BOULOGNE Mode tekening met pen en waterverf op karton door Jules David (1808 - Parijs - 1892). Gesigneerd links onder. Verso gedateerd/beschreven: "1877 / 3ème No d'Avril / No 16"?. Afmetingen: 29,1 x 23,5 cm. Het aquarel stamt uit een serie van modeontwerpen gemaakt door David voor het Parijse modetijdschrift "Le Moniteur de la Mode" ("Journal du Grand Monde. Modes, Illustrations, Patrons, Litterature, Beaux-Arts,Theatres"?). Hiervan bevinden zich verschillende exemplaren in het Musée des Arts Décoratifs (Pavillon de Marsan/Louvre). Jules David was leerling van Duval le Camus en ontving van Le Salon in 1885 een Mention Honorable. Dit werk komt uit de verzameling van Charlotte von Prybram-Gladona. Charlotte, habituée van de Beau Monde, werd in 1910 geboren te München en trouwde op vierentwintigjarige leeftijd met de Weense edelman Albin von Prybram-Gladona. De echtelieden ontmoetten elkaar tijdens de danslessen die Albin, twintig jaar ouder dan Charlotte, nam om fit te blijven (!). Zijn familie onderhield nauwe banden met Einstein, Schweitzer, Rilke en Thomas Mann, terwijl hij Johannes Brahms kende als "˜onkel Jo'. Toen Charlotte en Albin vlak voor het uitbreken van de Tweede Wereldoorlog verhuisden naar Parijs, verkochten zij noodgedwongen het leeuwendeel van hun meubelcollectie. Dat stelde hen echter wel in staat zich over te geven aan hun passie voor tekeningen, die beduidend minder plaats innamen. Het echtpaar keerde in 1969 terug naar Oostenrijk en vestigde zich in Salzburg. Albin overleed vijf jaar later, terwijl Charlotte er de hoge leeftijd van 92 bereikte. Prijs: Euro 950,-
 Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional seller
Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional sellerBook number: 1871
€ 985.00 [Appr.: US$ 1065.85 | £UK 838 | JP¥ 167166]
Keywords: David-- Jules
Baltics, Estonia, Lithuania - Joseph-Nicolas De l'Isle, 1745
MAP OF BALTICS FROM THE ATLAS RUSSICUS "DVCATVVM ESTONIA et LIVONIAE, TABVLA cumcursu Fluvii Dwiniae", copper engraving published in St.Petersburg in 1745 by Joseph-Nicolas De l'Isle. Original hand colouring. Size: approx. 50 x 58 cm. From the Atlas Russicus, the first complete printed atlas of Russia. Joseph-NicolasDe l'Isle, younger brother of Guillaume De l'Isle, was invited by Peter the Great to survey the vast empire of Imperial Russia. The enlightened Tzar also invited De l'Isle to found a school of Astronomy in St. Petersburg, and although Peter the Great died a year before De l'Isle arrived in St. Petersburg in 1726, he was successful in achieving both of his Imperial commissions. Together with his partner Ivan Kirilov they founded the school of Astronomy and began the immense task of surveying the Russian Empire. Eventually the two men parted company and Kirilov decided to publish his own incomplete atlas of Russia in 1734, eleven years before De l'Isle's French team finished its more comprehensive work. On his return to Paris in 1747, De l'Isle was able to construct his own observatory in the palace of Cluny, the same observatory later made famous by French astronomer Charles Messier. Price: Euro650,-
 Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional seller
Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional sellerBook number: 909
€ 650.00 [Appr.: US$ 703.35 | £UK 553 | JP¥ 110313]
Keywords: De l'Isle-- Joseph-Nicolas (1688 - 1768)
Marine, four parts of the day - Philip James de Loutherbourg, 1764
Seascapes "Le Matin" (The Morning), "Le Midi" (The Midday), "Le Soir" (The Evening), and "La Nuit" (The Night), four etchings from the series "Les Quatre Heures du Jour" made by Philippe Jacques de Loutherbourg in 1764. (Size: each approx. 12 x 19 cm. In one frame: 35 x 102 cm.) These seascapes are allegories of the four times of day. In the morning, the sun rises, marking the beginning of a new day. In the afternoon, there are high waves, and work must be done on board. In the evening, when the wind has calmed, it becomes tranquil, and a shepherd on the shore brings his animals back from the land. In the night, it is dark, a fire burns, and the sails hang out to dry. Philippe Jacques de Loutherbourg (1740-1812) is particularly known for his maritime art. De Loutherbourg apprenticed under genre and portrait painter Carle van Loo in Paris in 1755 and later under Francesco Casanova, specializing in battle scenes and marines. It is during his time with Casanova that he likely created these four etchings. De Loutherbourg created dramatic, naturalistic light effects. He was one of the pioneers of Romanticism and had a significant influence on the direction maritime painting would take in the early 19th century. He particularly influenced the young J.M.W. Turner, who greatly admired his work. Price: Euro 1.350,- (incl. frame)
 Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional seller
Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional sellerBook number: 4971
€ 1350.00 [Appr.: US$ 1460.81 | £UK 1148.5 | JP¥ 229111]
Keywords: de Loutherbourg-- Philip James (1740-1812)
Banten (Java) - Coenraet Decker, 1676
“De stadt Bantam.” Kopergravure vervaardigd door Coenraet Decker voor Wouter Schoutens “Oost-Indische Voyagie; Vervattende veel voorname voorvallen en ongemeene vreemde Geschiedenissen, bloedige Zee- en Landtgevechten tegen de Portugeesen en Makassaren” uitgegeven door Jacob van Meurs in 1676. Later met de hand gekleurd. Afm. 19 x 28,3 cm. Bantam was rond 1600 de belangrijkste havenstad van Java. Het was de eerste haven van de Indische archipel die door Nederlanders werd aangedaan. De koning van Bantam genoot geen absolute macht; zowel met zijn regent als met de plaatselijke havenmeester diende hij rekening te houden. Bantam was een rijke stad met een belangrijke markt, die werd bezocht door handelaren uit India, Perzië en China. Bantam gold in het begin van de 17de eeuw als belangrijkste handelsstad van de Indonesische archipel. Hier werden alle mogelijke waren uit geheel Azië samengebracht. Nederlandse schepen deden in 1596 Bantam voor het eerst aan. De Portugezen hadden hier al jaren een vaste positie op de markt. Zij wilden de greep op deze stad niet prijsgeven aan de Nederlandse nieuwkomers. Voor de Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie (VOC) waren vooral de specerijen van belang, met name peper. Zij probeerde tevergeefs met haar vestiging een sleutelpositie te verkrijgen. De Engelsen verhinderen dit en ook de plaatselijke regent werkte de VOC tegen, uit vrees dat zij een te groot overwicht zou krijgen op de markt. De conflicten stapelden zich op en de compagnie besloot uit te wijken naar het naburige Jacarta, dat later Batavia zou worden. De stad moest daarmee zijn leidende positie afstaan en Batavia werd het economische centrum van de VOC in Azië. De verhouding tussen de VOC en de sultan van Bantam bleef gespannen, omdat hij de compagnie dwarsboomde in haar poging de markt te domineren. Gedurende de hele 17de eeuw laaiden telkens nieuwe conflicten op tussen de VOC en Bantam, waaruit de compagnie steeds als overwinnaar naar voren kwam. In 1756 kwam Bantam definitief onder gezag van de compagnie. Op veertienjarige leeftijd ging Wouter Schouten (1638-1704) in de leer bij een chirurgijn. Hij monsterde hij in 1658 aan op een vaart naar Oost-Indië. Na een reis van een halfjaar kwam het schip aan op de rede van Batavia en Schouten vestigde zich in het Kasteel van Batavia.Terug in Nederland vestigde Schouten hij zich in 1665 als chirurgijn in Haarlem. Over zijn reizen in Oost-Indië publiceerde hij in 1676 drie reisverslagen. Hij maakte daarbij behalve van zijn eigen ervaringen en indrukken tevens gebruik van de bestaande literatuur. De Oost-Indische voyagie behoort, ook volgens tijdgenoot François Valentijn tot de beste reisverhalen die destijds zijn geschreven. Prijs: Euro 175,-
 Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional seller
Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional sellerBook number: 5314
€ 175.00 [Appr.: US$ 189.36 | £UK 149 | JP¥ 29700]
Keywords: Decker-- Coenraet
Amsterdam - Heinrich Dilcher, 1857
19de-eeuws Amsterdam Plattegrond van Amsterdam "naar de natuur geteekend en op steen gegraveerd door Heinrich Dilcher (1824-1855), gedrukt en uitgegeven door Seyffardts Boekhandel te Amsterdam." 2de uitgave uit of na 1857. Later met de hand gekleurd. Afm. (kaartbeeld) 41 x 66 cm. We zien de stad vanaf een hoog fictief standpunt in Amsterdam Noord. Op dit vogelvlucht gezicht zijn de grotere gebouwen met enorm gevoel voor detaillering weergegeven. De individuele huizen staan er minder nauwkeurig op. De kaart toont onder andere de in 1854 gedempte Goudsbloemgracht en het hoofdgebouw van Artis, dat in 1855 gebouwd werd. Het nationaal monument "De Eendracht", beter bekend als "Naatje van de Dam" en onthuld in augustus 1856, staat echter nog niet ingetekend. Onder deze 2de uitgave zijn zestien kolommen opgenomen met "Voorname Gebouwen". De kolommen worden gescheiden door naar boven wijzende pijlen. Als je de lijnen van de pijlen naar boven door zou trekken verdelen ze het kaartbeeld in stroken. De gebouwen die tegen de onderrand in de kolommen genoemd worden, staan ergens in de virtuele stroken daarboven. Sommige kolommen vermelden veel, andere mindere gebouwen. Kolom zestien bleef leeg. Het systeem is te zien als een voorloper van de later veel gebruikelijkere gridvlakken die normaal met A1 beginnen en die een corresponderend straatnamen-/gebouwenregister hebben. 19de-eeuws plattegronden als deze werden in kleine oplages gedrukt. Het waren gebruiksvoorwerpen op niet erg sterk papier bovendien. Inmiddels zijn ze zeer zeldzaam geworden omdat bijna alle exemplaren verloren zijn gegaan. Literatuur: Hameleers "Kaarten van Amsterdam", nr. 207 Prijs: Euro 1.250,-
 Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional seller
Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional sellerBook number: 4774
€ 1250.00 [Appr.: US$ 1352.6 | £UK 1063.25 | JP¥ 212140]
Keywords: Dilcher-- Heinrich (1824-1855)
England, from Robin Hood's Bay to Coquet Island - Waghenaer, 1596
Caerte der Noordt custe van Engelandt, beginnende van Robinhodes baij tot Cocket Eijlandt from the second volume of "Den Nieuwen Spieghel der Zeevaardt". Published in Leiden by Lucas Janszn. Wagehenaer, 1596. Coloured by a later hand. Size: 33 x 51 cm. This chart shows the Yorkshire, Durham and Northumberland coastlines from Robin Hood's Bay to Coquet Island. North is oriented to the right of the page. Part II of the "Spieghel ..." was first published in 1585 in Leiden by the Plantijn Press and this example of the map would appear to be a first edition - the title text is only in Dutch and text on the verso is also Dutch. The signature of the engraver, Doetecum, appears at lower right. The North Sea is decorated with sailing ships, sea monsters and an elaborate compass rose, while a scale of miles is also given at lower right. The " Spieghel der Zeevaardt " is unique among printed rutters of the sixteenth century, as it was the first to contain maps. Furthermore, it outranks any other rutter of the period with its splendid presentation of charts and text. As such, it stood out as a model for the folio pilot guides of the seventeenth century. Koeman writes; "Thanks to the unparalleled skill of the engravers Baptist and Ioannes Van Deutecom, the original manuscript maps were transformed into the most beautiful maps of the period. The composition and adornment have greatly contributed to the splendour of what originally were simple sketch charts; the typography of the Plantijn printing house further added to the quality of the book". Literature: Koeman IV, Wag 10A, 26d Price: Euro 1.650,-
 Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional seller
Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional sellerBook number: 1666
€ 1650.00 [Appr.: US$ 1785.43 | £UK 1403.5 | JP¥ 280024]
Keywords: Doetecum-- Ioannes van
Hungary - Johannes van Doeticum + Claes Jansz. Visscher, 1634
Nova et recens emendata totius regni Ungariae una cum adiacentibus et finitimis regionibus delineatio [A new and recent revised depiction of the whole Kingdom of Hungary, together with the adjacent and neighboring countries], copper engraving made by Johannes van Doetecum first published by Cornelis Claesz in 1596, here published by Claes Jansz. Visscher in 1634. Coloured by a later hand. Verso: blank. Size: 35,7 x 53,9 cm. Important early map of Hungary, centered on the course of the Danube River, from Hungary to Romania. The map extends from Maribor, Zagreb and Vienna in the west, to Sibiu, Pitesti and Fagaras in Romania. The double headed eagle of the Habsburg Monarchy in the middle bears the arms of Hungary. The map includes small coats of arms, bird's eye views of the cities and descriptions of the important battles. The lower banner explains that the towns and strongholds conquered by the Ottomans are marked with a crescent on the top and the Christian towns with a cross. It was only in 1699 that the Ottomans ceded nearly all of Ottoman Hungary. Price: Euro 1.350,-
 Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional seller
Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional sellerBook number: 1634
€ 1350.00 [Appr.: US$ 1460.81 | £UK 1148.5 | JP¥ 229111]
Keywords: Doetecum-- Ioannes van
Hemelkaart sterrenbeelden - Homann, Doppelmayr, 1742/48
HEMELKAART MET STERRENBEELDEN EN STERRENWACHTEN "Hemisphaerium Coeli Australe", kopergravure vervaardigd door Johann Baptist Homann naar het werk van Johann Gabriel Doppelmayr, afkomstig uit de Atlas Coelestis in quo Mundus Spectabilis uitgegeven te Neurenberg 1742 of 1748. Later met de hand gekleurd. Afm. 49,1 x 57,2 cm. Hemelkaart van het zuidelijk halfrond. De sterrenbeelden - waaronder het Zuiderkruis en Orion - zijn afgebeeld volgens de waarnemingen van de astronoom Johannes Hevelius, maar we zien ook exotischere sterrenbeelden zoals Pauw, Toekan en een prachtige eenhoorn met de naam Monoceros. De tabellen links en rechts geven een beschrijving van de sterrenbeelden. De randen van de kaart tonen de vier belangrijkste Europese sterrenwachten in Greenwich, Kopenhagen, Kassel en Berlijn. De stand van de sterren op de kaart is correct voor het jaar 1730. Doppelmayr (1677-1750) was professor in de wiskunde in Neurenberg en schreef over astronomie, geografie, cartografie, trigonometrie, zonnewijzers en wiskundige instrumenten. Homann (1664-1724), een voormalige Dominicaner monnik, was de belangrijkste en meest productieve Duitse cartograaf/uitgever van de 18de eeuw en vervaardigde kaarten en globes die opvielen zowel door hun geografische nauwkeurigheid als bijzondere esthetiek. Prijs: Euro 2.250,- (incl. lijst)
 Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional seller
Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional sellerBook number: 1029
€ 2250.00 [Appr.: US$ 2434.68 | £UK 1914 | JP¥ 381851]
Keywords: Doppelmayr-- Johann Gabriel (1677-1750)
Moon - Homann, Doppelmayr, Hevelius, 1742/48
IMPORTANT MAP OF THE MOON “Tabula Selenographica in qua Lunarium Macularum exacta Descriptio secundum Nomenclaturam … Hevelii quam Riccioli”. Copper engraving made by Johann Baptist Homann after Johann Gabriel Doppelmayr, from the Atlas Coelestis in quo Mundus Spectabilis published in Nuremberg in 1742 or 1748. Coloured by a later hand. Size c. 48,5 x 58 cm. The left hand lunar map, composed by Johannes Hevelius, is a considered a foundational map in the science of Selenography – or lunar cartography. This map first appeared in Hevelius’ 1647 work Selenographia which laid the groundwork for most subsequent lunar cartographic studies. Here the moon is presented as it can never be seen from Earth, at a greater than 360 degrees and with all visible features given equal weight. In this map Hevelius also establishes the convention of mapping the lunar surface as if illuminated from a single source – in this case morning light. The naming conventions he set forth, which associate lunar features with terrestrial locations such as “Asia Minor”, “Persia”, “Sicilia”, etc. were popular until the middle of the 18th century when Giovanni Battista Riccioli’s nomenclature took precedence. The Riccioli map, on the right, is more properly known as the Riccioli-Grimaldi map, after fellow Jesuit Francesco Grimaldi with whom Riccioli composed the chart. This map first appeared in Riccioli and Grimaldi’s 1651 Almagestum Novum. This was a significant lunar chart and offered an entirely new nomenclature which, for the most part, is still in use today. Curiously, though Riccioli, as a devout Jesuit, composed several treatises denouncing Copernican theory, he chose to name one of the Moon’s most notable features after the astronomer – perhaps suggesting that he was a secret Copernicus sympathizer? Other well-known lunar features named by Riccioli include the Sea of Tranquility where Apollo 11 landed and where Neil Armstrong became the first human to set foot on the moon’s surface 50 years ago. The upper left and right hand quadrants feature decorative allegorical cartouche work that include images of putti looking through a telescope and a representation of the ancient Greek Moon goddess Selene. Additional smaller maps show the moon in various phases of its monthly cycle. Below the map proper extensive Latin text discusses Selenography. This map first appeared Johann Baptist Homann’s 1707 Neuer Atlas and was later reissued as plate no. 11 in Doppelmayr’s important 1742 Atlas Coelestis, which was also published by Homann. Price: Euro 1.950,-
 Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional seller
Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional sellerBook number: 8516
€ 1950.00 [Appr.: US$ 2110.06 | £UK 1658.75 | JP¥ 330938]
Keywords: Doppelmayr-- Johann Gabriel (1677-1750)
North Holland - Johannes Dou, 1781
WANDKAART NOORD HOLLAND "'T Hoogheemraadschap vande Uytwaterende Sluysen in Kennemerlant ende West-Frieslant", kopergravure naar het ontwerp van Johannes Dou I, uitgegeven te Amsterdam bij Jacobus Nieuwenhoff in 1781. Later met de hand gekleurd. Vier bladen aaneen gemonteerd. Afm. 86 x 112 cm. De kaart is een typisch voorbeeld van Nederlandse waterschapscartografie. Om het in een diepe kom liggende Hollandse laagland tegen het water van zee en rivieren te beschermen, lagen er in West-Nederland een groot aantal waterschappen die ieder verantwoordelijk waren voor de waterstaatszorg in hun gebied. Om het waterbeheer zo efficiënt mogelijk te laten zijn, waren goede overzichtskaarten enorm belangrijk. Dijkgraaf en Hoogheemraden van het waterschap Uitwaterende Sluizen in Kennemerland en West-Friesland gaven landmeter/kaarttekenaar Johannes Dou I (1615-1682) opdracht hun grondgebied in het noordelijk gedeelte van Holland in kaart te brengen. Dou deed er 20 (!) jaar over en kwam in 1682 met een enorme kaart over zestien bladen. Twee jaar later was een kopie van de kaart over vier bladen klaar, alsmede een afbeelding op één blad. Alle drie de versies van de kaart werden gegraveerd door Koenraet Decker (1651-1709) een leerling van Romeyn de Hooghe en Abraham Deur. Hoewel hun namen slechts voorkomen op de zestien bladige uitgave is aangetoond, dat de gebruikte koperplaten vaker werden gekopieerd, zowel afzonderlijk als in sets van drie kaarten. Hoewel het kaartbeeld ongewijzigd bleef, zitten er kleine verschillen tussen de wapens van de waterschapsfunctionarissen. Aan de hand van de wapens op dit exemplaar van dijkgraaf Willem Winder en de hoogheemraden Willem Lodewijk Graaf van Nassau Bergen, Jacob van Twuijver, Cornelis Kuyper, Daniel Ras en rentmeester en secretaris Gualtherus George Gideon van der Mieden, kunnen we stellen dat deze kaart is verschenen in 1781. Johannes Dou I werd door het Hof van Holland als landmeter geadmitteerd op 10 september 1635. Hij genoot zijn opleiding aan de Leidse Universiteit. Na de dood van zijn vader in 1635 wordt hij samen met Steven van Broeckhuysen in vaste dienst aangesteld als landmeter van Rijnland. Vanaf 1637 was hij ook notaris. Literatuur: o.a. Donkersloot - de Vrij, Topografische kaarten van Nederland vóór 1750, p. 147-148, nr. 751. Prijs: Euro 3.250,-
 Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional seller
Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional sellerBook number: 5589
€ 3250.00 [Appr.: US$ 3516.76 | £UK 2764.5 | JP¥ 551563]
Keywords: Dou-- Johannes (1615-1682)
Amstelland - Gerrit Drogenham + Daniel Stoopendaal, c. 1720
WANDKAART VAN AMSTELLAND "Nieuwe accurate kaart van Amstellandt met een gedeelte van 't Sticht, Rhynlandt, en Noordhollandt: met de Ye stroom, en de banscheidingen van de steden en dorpen, daar in gelegen. Met de situwatie van alle de polders, molens, molen-wateringen, en scheidingen in die landen begrepen." Gemeten en getekend door Gerrit Drogenham (“Geometra”), gecorrigeerd door J. van Petersom (“geadmitteerd Landmeeter”), “in ‘t Koper gebragt” door Daniël Stoopendaal, voor het eerst uitgegeven rond 1720 door Nicolaas Visscher en in het tweede kwart van de 18de eeuw heruitgegeven door Reinier en Josua Ottens. In de tijd met de hand gekleurd, met latere toevoegingen. Afm. (prent) ca. 99 x 111 cm. Amsterdam was aan het eind van de 17e-eeuw gegroeid tot het centrum van de wereldhandel. Veel grond rondom de stad was eigendom van Amsterdammers. In de Middelpolder bijvoorbeeld, was in de 17e-eeuw ongeveer de helft van de grond in bezit van Amsterdamse instellingen, de andere helft was van particuliere Amsterdammers. In de Groot Duivendrechterpolder gold hetzelfde: omdat ook daar Amsterdammers en instellingen land hadden, moesten drie van de gekozen molenmeesters afkomstig zijn uit de stad. De stad kreeg op alle niveaus invloed op de processen die de inrichting van het platteland bepaalden: de bedrijfsvoering in de landbouw, poldervorming en waterbeheer, infrastructuur, dijkonderhoud en de aanleg van buitenplaatsen. De boerenbedrijven binnen een kilometer of vijf rond de stad, leverden verse melk. Nabijheid van de markt was noodzakelijk vanwege de bederfelijkheid van onbewerkte melk en deze boeren gingen met paard en wagen of schuiten dagelijks naar Amsterdam. De boeren daarbuiten, in een ruime cirkel rond de stad, produceerden boter en kaas. Ook hennepteelt was daar van belang. Hennepvezels dienden als grondstof voor de vervaardiging van touw en zeildoek. De zuidelijker gelegen Ronde Venen produceerden voornamelijk kaas. In de omgeving van Abcoude lag de nadruk op boterproductie. In een nog ruimere kring om de stad, vooral in het gebied boven het IJ, vond vetweiderij plaats. Na het rampjaar 1672 stagneerde de groei van de bevolking en stopte de economische groei. De landbouwprijzen daalden. Dat begon met de graanprijzen, kort daarna volgden ook de prijzen van zuivel. De loonkosten en polderlasten gingen tegelijkertijd omhoog. Het dieptepunt in de landbouw werd bereikt toen naast bovenstaande problemen ook nog veepest uitbrak, voor de eerste maal in 1713-1720. Vestingwerken markeren de grens van de stad maar niet die van de stedelijke functies. Activiteiten die te veel ruimte in namen of die lawaai, vervuiling, stank, rook, brand- of explosiegevaar veroorzaakten, werden verplaatst naar de rand van de stad of haar periferie. Tegen de stadsrand, binnen de stadswal waren industrieën gevestigd als lijnbanen verfproducenten, zwavelraffinaderijen, pottenbakkerijen en brandewijnstokerijen. Bedrijven die meer ruimte innamen of de sterke vervuiling veroorzaakten, zoals lakenramen [het opspannen en drogen van wollen stoffen], katoendrukkerijen en traankokerijen [voor de vervaardiging van lampolie en zeep] lagen buiten de stad. Sommige boeren werkten samen met linnenblekerijen. De blekers gebruikten grote hoeveelheden karnemelk en soms wei voor het ‘melken’ van linnen stoffen en garen. Karnemelk was een bijproduct van de boterproductie en wei van de kaas productie. Over land vormden de Overtoom en Amstelveenseweg de route naar Leiden en Den Haag en daarmee een redelijk drukke verkeersverbinding. De wegen vielen op in het landschap door de bomen die erlangs stonden. In het veen groeiden geen grote bomen. De wegen lagen hoger en daar stond op veel plaatsen een min of meer aaneengesloten bomenrij. Tot in de 18e-eeuw waren er in Amstelland geen bestrate wegen. Tot in het begin van de twintigste eeuw ging echter het meeste vervoer over water. De Amstel was de hoofdverkeersader door Amstelland. Er waren geregelde veerdiensten tussen de dorpen en de stedelijke markten en tussen de steden en dorpen onderling. Vanaf de 17e-eeuw is er ook de trekschuit, waarin plaats was voor zo’n 25 passagiers. Er ontstond een netwerk van pendeldiensten tussen de belangrijkste steden in de republiek. De kaart geeft de situatie weer van rond 1720. Veel van de meren in Holland zijn dan reeds ingepolderd. Het Haarlemmermeer, Legmeer, Langemeer en Horstermeer, hier nog op de kaart, worden pas in de 19de eeuw ingepolderd. Ten opzichte van de eerste uitgave van Nicolaas Visscher is de kaartinhoud bij de uitgave van de firma Ottens enigszins gewijzigd. Er zijn een aantal namen van bewoners van buitenhuizen langs de rivieren Amstel, Angstel, Bullewijk, Holendrecht en Vecht bijgeplaatst en/of gewijzigd. Een ander verschil is dat op de eerste uitgave dorpsnaam "Loendersloot" op de linker oever staat, op de tweede uitgave is deze verplaatst naar de rechter oever. Prijs: Euro 5.850,-
 Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional seller
Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional sellerBook number: 6123
€ 5850.00 [Appr.: US$ 6330.17 | £UK 4976 | JP¥ 992813]
Keywords: Drogenham-- Gerrit
Rotterdam harbour - Edward Duncan after William John Huggins, 1842
ROTTERDAM HARBOUR IN THE 19TH CENTURY "Ships of the General Steam Navigation Company, off Rotterdam. The Giraffe of 500 Tons arriving, and The Ocean of 600 Tons leaving, with Her Majesty's Mails". Etching with aquatint made in 1842 by Edward Duncan after the design of marine painter William John Huggins. With original hand colouring. Size: approx. 35,5 x 60 cm. Starboard stern view of the 500-ton paddle steamer The Giraffe entering Rotterdam under steam. The British ensigns are flying on the stern gaff and the fore mast; the General Steam Navigation Company flag is flying on the stern mast. People are depicted on the deck. Crossing the bows of the Giraffe, is the Ocean paddle steamer leaving port under steam. She also flies the ensign and GSNC company flags. A small rowing vessel, with two men and two women is shown in the bottom right foreground. A cityscape of Rotterdam shoreline can be seen in the background complete with churches, moored shipping and a windmill. Both paddle steamers were launched in 1836 and used as mail steamers by the British General Steam Navigation Company (GSNC). The Giraffe later served during the American Civil War. The GSNC, incorporated in 1824, was London's foremost short sea shipping line for almost 150 years, and the oldest shipping company in the world to begin business with steamships. The GSNC experimented with services to Lisbon, Portugal and to Gibraltar, and even to Africa and the Americas, but specialised in links with ports in Britain (including Lowestoft and Great Yarmouth) and northwest Europe. Prijs: 1.250,- (incl. frame)
 Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional seller
Inter-Antiquariaat Mefferdt & De JongeProfessional sellerBook number: 1386
€ 1750.00 [Appr.: US$ 1893.64 | £UK 1488.75 | JP¥ 296995]
Keywords: Duncan-- Edward
Previous page | Pages: 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | - Next page